Table of Contents
ToggleThe disc diffusion method of Kirby and Bauer is one of the most adaptive qualitative approaches which is often employed to determine antimicrobial susceptibility to an antibiotic. The antimicrobial susceptibility test determines how sensitive a bacteria or fungus is to one or more antimicrobial compounds simultaneously. The results of this test aid in choosing the drug(s) that would most successfully treat an infection. Other methods to test antibiotic sensitivity include dilution test, E test/Epsilometer test, etc.
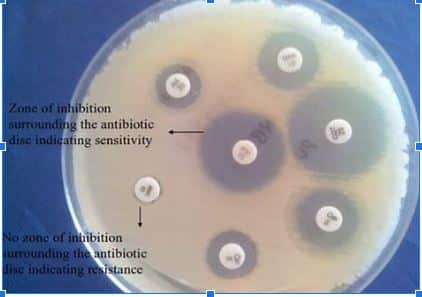
In accordance with CLSI standards, the zone of inhibition is measured based on which microbes can be categorized as sensitive (S), intermediate (I), or resistant (R).
Principle of Antimicrobial susceptibility test by disc diffusion method
Principle of Antimicrobial susceptibility test by disc diffusion method
This technique is based on the idea that an antibiotic-infused paper disc when placed over agar already seeded with the test bacterium, develops a concentration gradient following the radial diffusion of the antibiotic. The clear zone surrounding the disk is measured to assess microbial susceptibility.
Disc diffusion method procedure
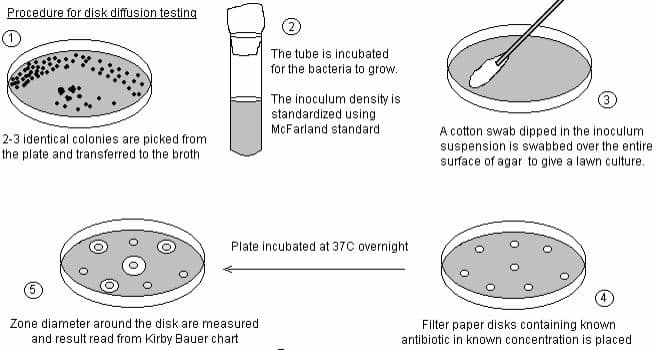
To evaluate the susceptibility of microbes towards different plant extracts, secondary metabolites, nanoparticles, antibiotics, etc, researchers typically perform the agar disc diffusion method. The steps for the paper disc diffusion method are listed below.
- Firstly, the Muller Hinton Agar (MHA) plates and Muller Hinton Broth (MHB) are prepared.
- The bacteria to be tested are then introduced into these broths by inoculating a loop and incubated at 37 degrees Celsius for 24 hours.
- Before beginning the test, sterilize the area with disinfectant and turn the burner on.
- Label the MHA plates (petri-dish) precisely with the organism name and adjust the turbidity of bacterial suspension taking McFarland Standards as a reference. Using a sterile cotton bud, swab the surface of the plate completely with continuous rotation to create a uniform layer of bacteria and let it dry for ~5 minutes.
- Flame sterilize the forceps with alcohol before picking up the discs.
- Now, place the disc carefully over the seeded plate and tap lightly.
- Discs should be separated apart by ≥24mm.
- Incubate the plates at 37-degree celsius for 24 hours.
- After incubation, the zone of inhibition is measured and compared with CLSI guidelines to evaluate the outcomes.
Advantages of the disc diffusion method
- It is an affordable and versatile method that enables growth visibility.
- It carries the possibility of performing a direct susceptibility test (DST).
- This test allows us to choose the best antibiotics to treat an ailment.
- It is simple to perform and easy to interpret.
- Provides us with information on important microbes for public health.
Disadvantages of the disc diffusion method
- The dearth of automation or mechanization in this test is one of its limitations.
- Some slow or fastidious organisms cannot be tested effectively by this method.
Agar well diffusion Vs disc diffusion method
Agar well diffusion method is an in vitro antimicrobial activity test in which the extract solution to be tested is poured into a well made on the agar medium. Whereas, the test solution is deposited on a filter paper disc and placed on the agar medium in the agar disc diffusion method.
FAQs/MCQs
Why is Mueller-Hinton agar used for disc diffusion methods?
The MHA is a nonselective and non-differential medium. It is routinely used for antibiotic susceptibility testing by the disc diffusion method because it is a “loose” agar and ensures effective diffusion of antibiotics.
What factors affect the size of a zone of inhibition in a disk diffusion assay?
The drug’s solubility, the rate of its diffusion through agar, the thickness of the agar medium, the drug concentration in the disc, and the size of the paper disc are some variables that influence the size of the zone of inhibition in this assay.
Why is it necessary to match the bacterial inoculum against a 0.5% McFarland standard?
It helps to maintain and ensure that the number of bacteria will be within a specified range to standardize microbial testing.
What is the difference between antimicrobial susceptibility and antimicrobial activity?
The “Antimicrobial susceptibility test” is employed to choose the antibiotic that will effectively treat a bacterial infection in vivo. Whereas, antimicrobial activity refers to all bioactive components (agents) that can impede bacterial growth or even kill them.