Table of Contents
ToggleThe urease test is used to distinguish urease-positive organisms from other species, such as Proteus. It can also be used to find out if Helicobacter pylori is present. Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans, two yeasts, can be distinguished with this test. Urease test is the most common and important biochemical test for the differentiation of bacteria.
Urease Test definition
The urease test reveals the presence of microbes that can hydrolyze urea to create ammonia and carbon dioxide. It is mainly utilized to distinguish other Enterobacteriaceae from Proteeae that are urease-positive. To find urease activity, two media types are frequently utilized. Urease activity in a number of microorganisms is found using Christensen’s urea agar. The main application of Stuart’s urea broth is the distinction of Proteus species.
History of urease test
Christensen created urea agar in 1946 to help differentiate enteric bacilli. The urease test is used to assess an organism’s capacity to digest urea by producing the enzyme urease. Since urease was the first enzyme to crystallize (1926), it has historical significance in biochemistry. The discovery of nickel in the active site of urease in 1975 was the first proof that this metal has a biological function.
Principle of Urease Test
An enzyme called urease, which is constitutively produced, breaks down urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Ammonia and CO2 are produced during the hydrolysis of urea by the constitutively expressed enzyme urease. The solution becomes more alkaline due to the creation of ammonia, and the pH change is indicated by the color change of phenol red from light orange at pH 6.8 to magenta (pink) at pH 8.1.
Requirement for urease test
Test organism for Christensen’s urea agar
Immunization wire or wooden stick
Bunsen stove
Incubator
test-tube rack
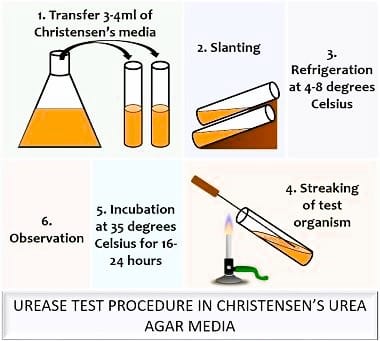
Protocol of urease test
The procedure for urease test are discuss below:
- A part of a well-isolated colony is spread on the surface of a urea agar slant, or inoculate the slant with one to two drops of an overnight brain-heart infusion broth culture.
- For 18 to 24 hours, the tube is incubated at 37° C in free air with the top loosely on.
- Variations in the infected medium’s color is observed.

Quality control for urease test
Proteus mirabilis is a positive control (PC) for urea-positive bacteria.
Escherichia coli (bacteria that produce no urea) is the negative control (NC).
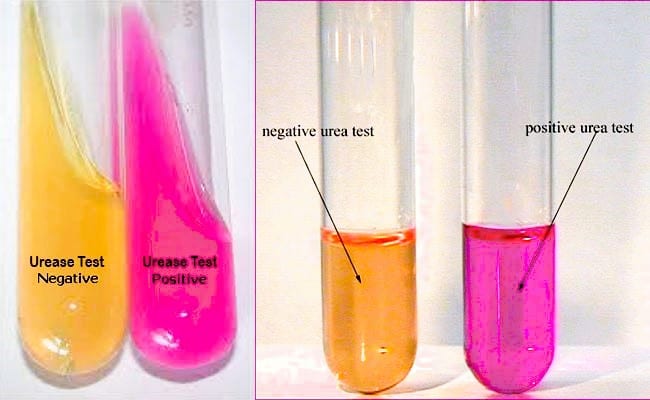
Results and Observation
- color of the slant shifts from light orange to magenta/bright pink/red when an organism develops a urease enzyme.
- The agar slant and butt remain light orange (medium keeps original hue) if an organism does not make urease.
Application of urease test
Numerous pathogenic bacteria include the virulence component urease. It is crucial for the colonization of a host organism and for keeping bacterial cells alive in tissues. Urease has a harmful effect on human cells as a result of its enzymatic activity.
Rapid urease test