Table of Contents
ToggleRibozymes are the enzymes of RNA molecules. They are the enzymes of RNA which act as catalyst a chemical reaction. It work as same as protein enzymes. They are also known as catalytic RNA and generally found in ribosome where they help in connect amino acid to form chain of proteins.
Definition of Ribozymes
Ribozymes: Definition
Dictionary meaning
noun, plural, ribozymes
RNA molecules that act like a biocatalyst or enzyme in the amino transferase activity of the ribosome and in the breakage of its own or another RNA molecules.
Ribozymes are RNA molecules or RNA–protein complexes that are catalytically active, with the catalytic activity coming only from the RNA. The name “ribozyme” describes both the ribonucleic acid nature and the enzymatic activity simultaneously. The genomes of all organisms throughout the domains of life contain ribozymes.
History of Ribozymes
First ribozyme was discovered in early 1980s. RNA act as biological catalyst and as well as genetic material. The only known biological catalysts prior to the discovery of ribozymes were enzymes, which are classified as catalytic proteins. Leslie Orgel, Francis Crick, and Carl Woese were the first to propose that RNA may function as a catalyst in 1967. The finding that RNA can create intricate secondary structures served as the foundation for this theory.
These ribozymes were discovered in the RNA component of the RNase P complex, which is involved in the maturation of pre-tRNAs, as well as the intron of an RNA transcript that had cut itself off from the transcript. The “discovery of catalytic properties of RNA” earned Cech and Sidney Altman a share of the 1989 Chemistry Nobel Prize. Kelly Kruger et al. initially described ribozyme in a 1982 publication that was published in Cell.
Location of ribozyme:
They are generally found in selected bacteria, viruses, lower eukaryotes, plant organelles.
Properties of Ribozymes
The properties of ribozyme are:
- Ability to catalyze biological reaction
- RNA splicing
- Transfer RNA biosynthesis
- Viral replication
Examples of Ribozymes
- Smaller ribozyme: hammerhead, viroid, riboswitch ribozyme
- Larger ribozyme:
Function of Ribozymes
The function of ribozyme are:
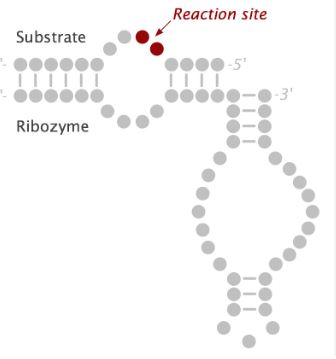
Through their ability to separate from the cleavage products and attach to another target molecule, ribozymes can cleave more than one copy of the target RNA and inactivate it without the aid of the host cell’s machinery.
Classes of Ribozymes
Generally ribozyme are classified in 12 classes.
- small self cleaving RNAs (9 classes)
- group I entrons
- Group II introns
- Ribonuclease P
They are further categorized on the basis of size:
- small ones, which usually donot require metal ions for activity, vary from from 10-150 nucleotides.
- larger ones which can be few thousand of nucleotides.
Differences between Ribozymes and Protein enzymes
- Composition and structure
Ribozyme are made from RNA and are the component of RNA. While Protein enzyme are made from amino acid and from complex structure.
2. Function
Ribozyme are used in catalysis in chemical reaction in RNA world. and can catalyze the cutting and joining of phosphodiester bond in RNA molecules. While protein enzymes used in various cellular process. For example amylase catalyze the breakdown of starch into glucose in digestion.
Hammerhead ribozyme
An endonucleolytic (self-) cleaving tiny catalytic RNA motif is known as the hammerhead ribozyme. It consists of three helices around a catalytic core of conserved nucleotides, two of which establish critical tertiary connections for rapid self-scission in physiological settings.
Hairpin ribozyme
A brief segment of RNA with ribozyme-like properties is called the hairpin ribozyme. Similar to the hammerhead ribozyme, it is present in plant virus RNA satellites. It was initially discovered to catalyze self-cleavage and joining (ligation) events in the minus strand of the tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV) satellite RNA, which transforms the byproducts of rolling circle virus replication into linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. In that a metal ion is not necessary for the reaction, the hairpin ribozyme and the hammerhead ribozyme are comparable.
FAQs/MCQs
What is ribozyme?
Ribozyme are the RNA molecule catalyst act as RNA slicing found in ribosome.
What are the example of ribozyme?
The example of ribozyme are hammerhead, viroid.
Where is ribozyme found?
They are found in selected bacteria, viruses.
How many classes are ribozyme are there?
There are 12 classes of ribozymes.
What is the function of ribozymes?
Ribozymes perform a number of essential tasks for molecular biology, such as splicing RNA transcripts and creating peptide bonds during translation, in addition to their responsibilities as endonucleases.
Who first discovered ribozyme?
Ribozyme was first discovered by Tom Cectislab and Atman.
References
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-are-Ribozymes.aspx