Table of Contents
ToggleLAP Test stands for leucine amino peptidase. LAP is an example of an enzyme-class protein. This enzyme is typically present in the placenta, blood, urine, bile, and liver cells. In order to determine whether your liver is damaged, your doctor could perform this test. If you have a liver tumor or liver cell injury, too much LAP is released into your blood. It is generally involved in tumor cases.
What is LAP Test?
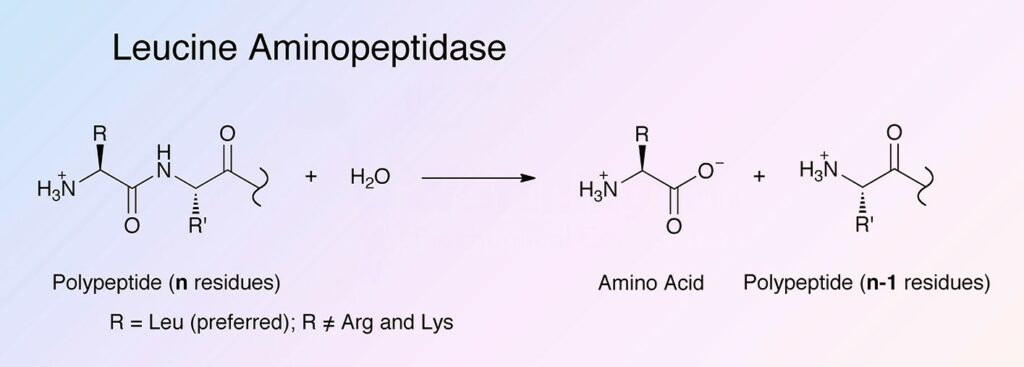
Leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) is an exopeptidase that facilitates the hydrolysis of amino acid residues from polypeptide chains’ amino termini. Because of their function in protein degradation, LAPs are widely present, ubiquitous in nature, and of crucial biological value.
Principle of LAP Test
One of the quick tests used to find leucine amino peptidase is called the leucine amino peptididase (LAP) test. The LAP test is typically used to characterize gram-positive, catalase-negative cocci, particularly non-beta hemolytic cocci.
Composition of LAP
The homohexamer of cattle eye lens LAP. Alpha and beta structures are intermingled in the monomer. Six active sites line a disk-shaped cavity inside the hexamer, which has six of them. Solvent routes provide entry into this cavity. The enzyme’s inability to cleave longer peptides or proteins is explained by this characteristic (Kim et al. 1974). The two zinc ions in each active site are connected by a single water ligand (Burley et al. 1991; Sträter and Lipscomb 1995).
Source: http://universe84a
Alternative name
Serum leucine aminopeptidase; LAP – serum
History of LAP test
An enzyme discovered in the mucosa of pig intestines was said to cleave leucylglycine around 20 times more quickly than it did glycylglycine in 1929. Dipeptidase II was the name given to this enzyme (Linderstrm-Lang 1929). Aminoleucylpeptidase was the name given to it afterwards (Holter 1979; Sträter and Lipscomb 2004).
Leucylpeptidase was the name given to the enzyme when it was largely purified in 1936 (Johnson et al. 1936). Additionally, Johnson et al. showed that manganese and magnesium both activate LAP.
Why lap test is done?
LAP is an example of an enzyme-class protein. This enzyme is typically present in the placenta, blood, urine, bile, and liver cells. In order to determine whether your liver is damaged, your doctor could perform this test. If you have a liver tumor or liver cell injury, too much LAP is released into your blood.
Protocol of LAP Test
- The disk is placed on a slide or a petri dish.
- By the help of disk a loopful of distilled water to moisten but not completely submerge.
- The claimed isolate is spread on a sterile stick or loop.
- 5 minutes of room temperature incubation is required.
- Once the cinnamaldehyde reagent has been added, wait two minutes before checking the color.
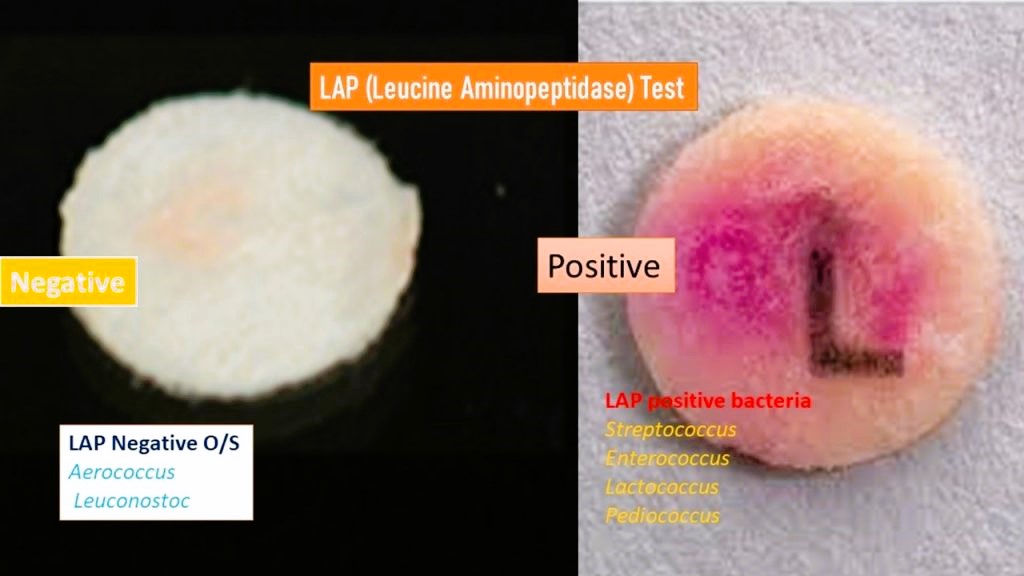
Positive lap test
On adding reagent, if it turns into reddish red to purple, it shows positive test.
Negative lap test
No color change.
Application of LAP Test
The application of lap test are pointed below:
- Sequence analysis
- Control of serum in protein studies
- Identification of L-peptides and amino acid amides with leucine or proline at the N-terminus
- Cleavage of albomycins’ deferriform
- Gamma-methyl and gamma-fluoroglutamic acids’ resolution
References
https://www.healthline.com/health/leukocyte-alkaline-phosphatase#purpose