Table of Contents
ToggleCoordination Number is defined as the number of atoms, ions, or molecules attached to the central atom. The atoms, ions, or molecules attached to the central atom, ion, or molecule are ligands. In other words, the coordination number is equal to the total number of donor atoms/ligands that are attached to the central metal atom.
Alfred Werner coined the term “coordination Number” to describe the total number of bonds between the ligands and the metal atom. Coordination numbers typically range from 2 to 12, with the most prevalent being 4 (tetracoordinate) and 6 (hexacoordinate).
Calculation of Coordination Number
For crystals molecules, the value of the coordination number is determined in different ways. The value is determined by the relative sizes of the central atom and ligands, as well as the charge derived from an ion’s electronic configuration.
Some of the steps to identify the coordination number of complexes are:
- Determine central atom in the complex.
- Find the atom, molecule, or ion that is the closest to the central metal atom.
- Add the number of atoms of the closest atom/molecule/ions together.
- Find the total number of atoms that are closest to the central atom. Add the two values if the metal has two bonded atoms.
The coordination number in polyatomic molecules or ions is calculated by simply calculating the number of ligands or atoms, ions, or molecules attached to the central metal atom (except the number of chemical bonds).
In coordination complexes, only the sigma bond of ligands coordinated with central atoms are considered.
Coordination Number Examples
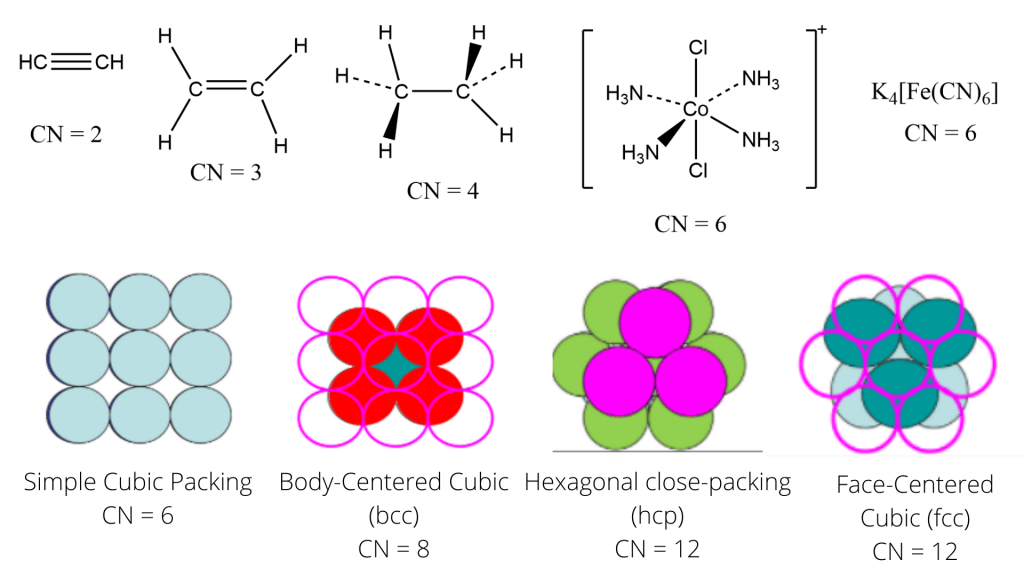
Geometry based on Coordination Number
The molecular geometry of the coordination complex can be deduced using the coordination number of the central metal atom/ion. Based on the coordination number, the molecular geometry of some of the coordination compounds are given as follows:
| Coordination Number (CN) | Molecular Geometry/Structure | Examples |
| 2 | Linear | [Hg(NH3)2]+ |
| 3 | Trigonal planar | [AgI3]– |
| 4 | Tetrahedral | Ni(CO)4 |
| 4 | Square Planar | [Cu(NH3)4]2+ |
| 5 | Trigonal bipyramidal | Fe(CO)5 |
| 6 | Octahedral | [Mn(H2O)6]2+ |
| 6 | Simple Cubic Packing | NaCl |
| 8 | Body-centered cubic (BCC) | CsCl |
| 12 | Hexagonal close packing (HCP) | The hcp structure is very common for elemental metals and some examples include beryllium, cadmium, magnesium, titanium, zinc, and zirconium. |
| 12 | Face centered cubic (FCC) | Metals with the fcc structure include aluminum, copper, nickel, gamma iron, gold, and silver. |
Similarly, some of the structures based on the coordination Number are:
| Coordination Number | Structure | Examples |
| 8:4 | Fluorite structure | CaF2 |
| 4:8 | Anti-fluorite structure | Na2O |
| 6:3 | Rutile structure | TiO2 |
Coordination Number Video
MCQs/FAQs
Coordination number of face-centered cubic (fcc)
The coordination number of face-centered cubic (fcc) is 12.
Coordination number of bcc
The coordination number of bcc is 8.
Coordination number of hcp (hexagonal close packing)
The Coordination number of hcp (hexagonal close packing) is 12.
Coordination number of NaCl
The Coordination number of NaCl is 6.
Which metallic crystal structure has a coordination number of 8?
Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) has a coordination number of 8.
The coordination number of copper in cuprammonium sulphate is
The coordination number of copper in cuprammonium sulphate is 4.
rock salt coordination number
The coordination number of rock salt is 6.
Simple cubic lattice coordination number
The Simple cubic lattice has a coordination number of 6.
Coordination number of iron in ferrocene
The Coordination number of iron in ferrocene is 10.
Coordination number of the central metal atom
The coordination number of the central metal atom is the number of ions, atoms,s, or molecules attached to it.
CaF2 crystal structure coordination number
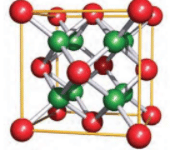
CaF2 crystal structure coordination number is 8:4
coordination number of rutile
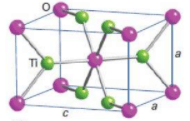
The coordination number of rutile is 6:3
coordination number of ethylenediamine
The coordination number of ethylenediamine is 6 as it is a bidentate ligand.
ruthenium coordination number
The most common coordination number of ruthenium is 6.