Table of Contents
TogglePolysaccharide from the name itself it is clear that poly means many, different, and saccharide means sugar or carbohydrates. Just like monosaccharides and disaccharides. In our previous article, we have already talked about disaccharides, their classification, function, etc now we are going to study polysaccharides.
Polysaccharide definition
What exactly is the definition of polysaccharide? They are long chains of monosaccharide molecules that make up carbohydrates. These complex biomacromolecules serve as a crucial energy source for animal cells and as a structural element of plant cells. The term “homopolysaccharide” refers to a type of polysaccharide made up of many molecules of a single sugar or sugar derivative (homoglycans). The stored carbohydrates for both plants and animals, starch and glycogen, are homopolysaccharides made of glucose, as is cellulose, a crucial structural element of the majority of plants.
Characteristics of polysaccharides
The characteristics of polysaccharides are:
- They are formed from the chain of one or more monosaccharides.
- They are generally not sweet in taste.
- Talking about solubility, they are insoluble in water.
- They are hydrophobic in nature.
- They have higher molecular weight.
Structure of polysaccharide
As is well known, a polysaccharide is formed by the same mechanism as monosaccharides—glycosidic linkages. A carbon ring and an oxygen molecule are joined together to form a bond. A bond is formed when one molecule’s carbon loses a hydroxyl group and another monosaccharide’s hydroxyl group loses a hydrogen atom. Due to the release of one oxygen molecule and two molecules of hydrogen, the reaction is known as a dehydration reaction.
Classification of polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are generally classified into two classes. They are discussed below.
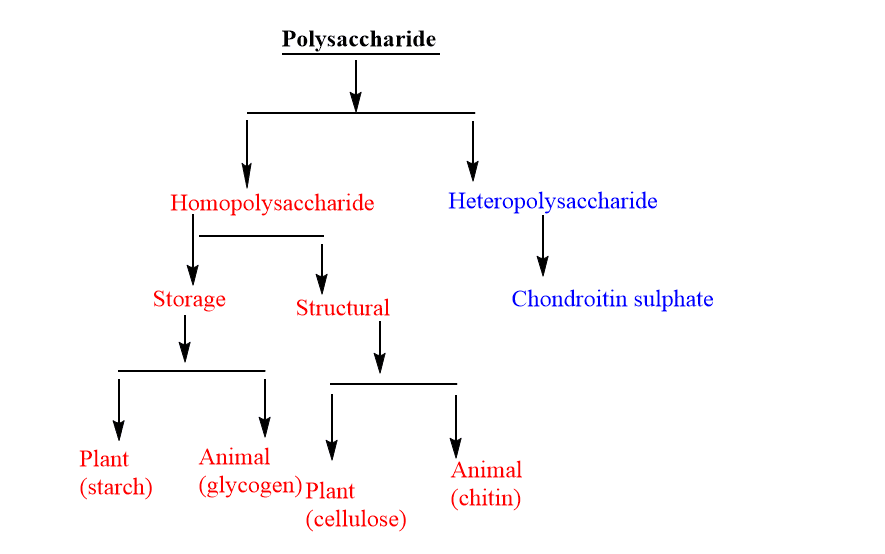
Homopolysaccharides
Homopolysaccharides are carbohydrates made up of one type of monosaccharide. Examples are starch, cellulose, glycogen
Heteropolysaccharides
They are made up of two or more types of monosaccharides. Examples are hyaluronic acid.
Some examples of homopolysaccharides:
- Glycogen: A long chain of molecules makes up this substance. Animals and fungi both contain it.
- Cellulose: Plants use cellulose to build their cell walls. It consists of extended chains of -glycosides.
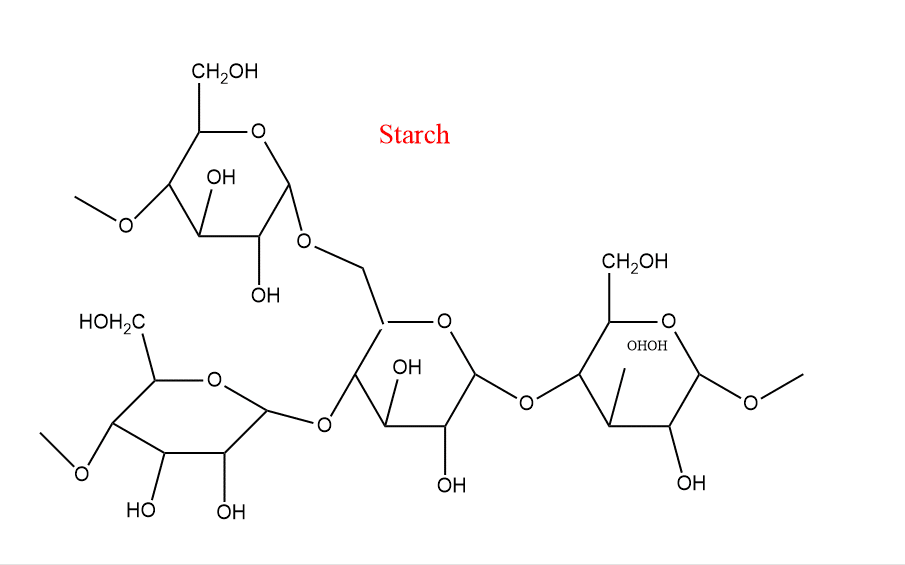
- As amylose and amylopectin condense, starch is formed. Major sources of it include plants, fruits, seeds, etc.
- The fructofuranose molecules that makeup inulin are connected in chains. Dahlia, artichoke, and other plant tubers contain it.
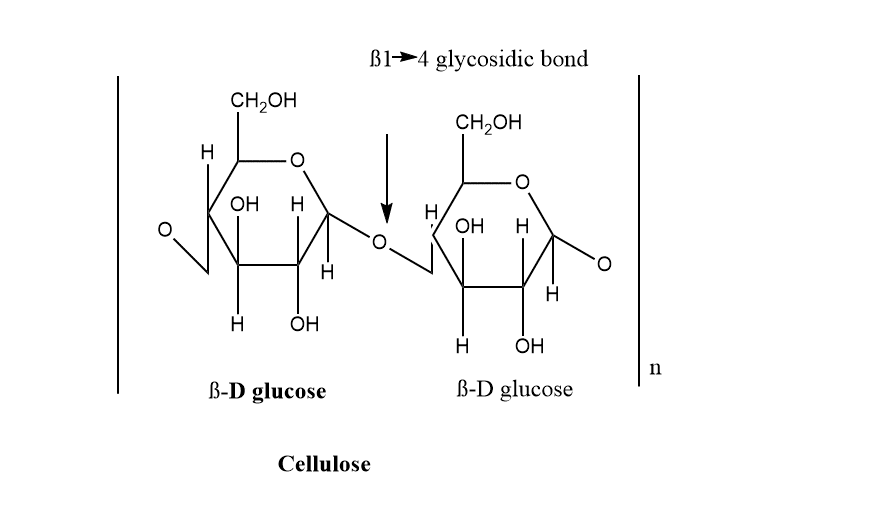
Some examples of heteropolysaccharides are:
- D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine are the two components that make up hyaluronic acid. It is present in the skin and connective tissues.
- D-glucuronic acid, L-iduronic acid, and N-sulfo-D-glucosamine are the main components of heparin, which is mostly found in mast cells and blood.
- D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-4-O-sulfate are two of the sugars that make up chondroitin-4-sulfate. The cartilages contain it.
- N-acetyl-hexosamine, D-mannose, and D-galactose are the polysaccharide’s component sugars in gamma globulin. It is found in the blood.
Function of polysaccharide
- It stores energy the same as other saccharides.
- In both animals and plants, polysaccharides act as a structural organization.
- The most prevalent polysaccharide used by plants for storage is starch, which is converted to maltose.
- For instance, sulfate polysaccharides have anti-HIV, anti-herpes, and anti-hepatitis virus activity as well as immunomodulatory, anticancer, antithrombotic, anticoagulant, anti-mutagenic, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties.
MCQs/FAQs
What are polysaccharides?
A kind of carbohydrate (such as glycogen, cellulose, or starch) whose molecules are made up of many sugar molecules bound together.
What are the two types of polysaccharides?
The two types of polysaccharides are homo and heteropolysaccharides.
Are polysaccharides sugar?
In nature, polysaccharides are a common type of biopolymer. These are simple sugar polymers, which are monosaccharides joined by glycosidic connections. Different kinds of polysaccharides exist.
Why they are addressed as polysaccharides?
An enormous molecule comprised of numerous smaller monosaccharides is known as a polysaccharide. Like glucose, monosaccharides are simple sugars. These tiny monomers are joined by special enzymes to form enormous sugar polymers or polysaccharides. A glycan is another name for a polysaccharide.