Table of Contents
ToggleCatalase test is the another important biochemical test for the separation of different variety of bacteria. Catalase-producing microbes are found using this technique to identify them. Hydrogen peroxide is detoxicated by this enzyme by converting it to water and oxygen gas. A catalase positive result is seen by the bubbles created when oxygen gas is produced.

What is Catalase test?
Catalase Test is a typical enzyme found in almost all living things exposed to oxygen, including bacteria, plants, and mammals. It helps hydrogen peroxide break down into water and oxygen. It is a crucial enzyme in preventing reactive oxygen species (ROS) from oxidatively harming the cell.
Principle of Catalase test?
Hydrogen peroxide is broken down into oxygen and water by the catalase enzyme. When a little inoculum is added to hydrogen peroxide and the rapid construction of oxygen bubbles takes place, it is clear that the enzyme is present in the bacterial isolate.
.A tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 amino acids long, makes up catalase. The enzyme may interact with hydrogen peroxide thanks to its four heme groups that contain iron. The rate of reaction does not significantly change between pH 6.8 and 7.5, which is around the optimal pH for human catalase and has a pretty broad maximum. Depending on the species, the pH ideal for other catalases ranges from 4 to 11. The ideal temperature differs depending on the species.
Reagent Used
The different reagents used in Catalase test are:
- Hydrogen Peroxide 3%
- HPLC grade water
Protocol of catalase test
The protocol for the catalase test are discussed below:
- The glass slide is first clean, without any contamination and must be dry
- Few drops of hydrogen peroxide is placed in glass slide.
- And few colonies are immersed in glass slide contating hydrogen peroxide
- The production of bubbles is seen
- Hydrogen peroxide is converted into water and oxygen, if bubbles are seen
- Dispose the slide due to dangerous effect of hydrogen peroxide
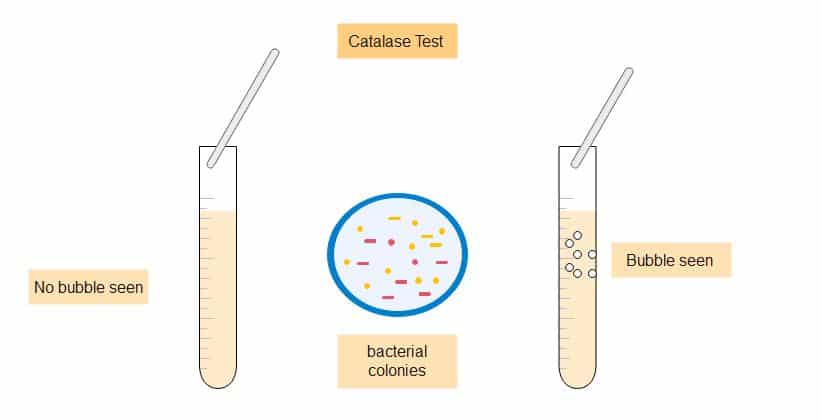
Positive Catalase test
The bacteria are catalase positive if bubbles form as a result of oxygen gas generation.
The organism is referred to as “catalase-positive” if the mixture creates bubbles or froth. Micrococci and Staphylococci are catalase-positive bacteria. The family Enterobacteriaceae (Citrobacter, E. coli, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Shigella, Yersinia, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia), Pseudomonas, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, and Rhodococcus equi are among the other organisms that are catalase-positive.
Negative Catalase test
The bacteria are catalase negative if no bubbles form. Catalase is present in Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. but not in Streptococcus and Enterococcus spp.
Catalase Vs Peroxidase test
Its depend upon the types of compounds they break down. Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Peroxidase helps to break down either compounds containing oxygen, such as organic peroxide.
Application of catalase test
The catalase test makes it easier to find this enzyme in bacterial samples. For separating catalase-positive Micrococcaceae from catalase-negative Streptococcaceae, it is crucial. While its main application is in the differentiation of genera, it can be helpful in the speciation of some gram positives.
References
https://www.uwyo.edu/molb2021/virtual-edge/lab
Johnson M. “Catalase Production”. Biochemical Tests