Table of Contents
ToggleCaffeine: What exactly is Caffeine?
Typically found in tea, coffee, and cacao plants, caffeine is a natural stimulant. It functions by energizing the brain and central nervous system, assisting you in maintaining your alertness and delaying the development of fatigue.

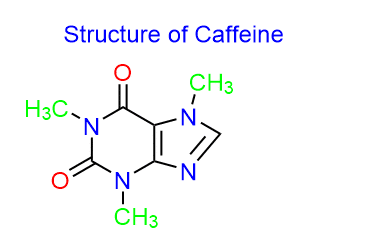
Caffeine chemical formula
Caffeine is a trimethylxanthine and a purine alkaloid that stimulates the central nervous system (CNS). It is also known as methyl theobromine, 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine, 7-methyltheophylline, guaranine, or theine and has the molecular formula C8H10N4O2. It appears as a tasteless, white, crystalline purine with no odor.
What are alkaloids?
Any member of the group of naturally occurring bases that include organic nitrogen is known as an alkaloid. On both humans and other animals, alkaloids have a variety of physiological effects that are significant. The alkaloids morphine, strychnine, quinine, ephedrine, and nicotine are well-known examples.
How does Caffeine works?
When caffeine attaches to adenosine receptors, adenosine cannot bind to the receptor. The release of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, dopamine, acetylcholine, serotonin, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid is indirectly impacted by the blocking of adenosine receptors (GABA).
Benefits of Caffeine
The benefits of having caffeine in the right amount are:
- Coffee is packed with compounds that could protect against diseases like Alzheimer’s and heart disease, which are more prevalent among women.
- When you think of coffee, the first thing that springs to mind is caffeine. However, according to nutritionists from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, coffee also contains antioxidants and other potent compounds that may lessen internal inflammation and offer protection against disease.
- You could live longer.
- Your body can produce glucose in a better way.
- You are less likely to have cardiac arrest.
- In addition to lowering the risk of acquiring Parkinson’s disease, caffeine may also improve movement control in those who already have the disorder.
- Dark roast coffee reduces DNA strand breaks, which happen naturally but can cause cancer or tumors if your cells don’t repair them.
- Women who consume at least one cup of coffee each day had a lower risk of developing stroke, which is the fourth largest cause of death for females.
Caffeine in tea and coffee
Numerous variables can affect how much caffeine is present in coffee and tea. However, an 8-ounce cup of brewed coffee has about 100 milligrams of caffeine in it, according to the Mayo Clinic. (Instant coffee and espresso have less.) Black tea, in contrast, contains about 50 mg of caffeine in an 8-ounce cup.
Comparison of caffeine in different drinks
Black tea has between 14 and 70 mg of caffeine and Coffee contains between 95 and 200 milligrams. Between 24 to 45 mg of caffeine are present in green tea while White tea has 6 to 60 mg of caffeine.
Caffeine in skin care products
Caffeine can be used as scrubbing for skin whitening etc. Caffeine lowers blood flow to the skin, giving it a brighter, tighter appearance, according to Dr. Hsu. It’s frequently used in face care, eye care, and even body care products as an anti-aging or wrinkle-smoothing component. Proper formulation is the secret to making skin-care products effective.
Since caffeine is an antioxidant, it is known to shield skin from the chemicals known as free radicals, which break down collagen and result in wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of sagging, sallow skin.
How does caffeine affect your sleep?
The stimulant’s most evident side effect is that it can make it difficult for you to go to sleep. According to one study, caffeine can make your body clock run later. Your overall sleep time will be shortened by these consequences. Additionally, caffeine can lessen the quantity of deep sleep you get.
The benefit of caffeine before a workout
Numerous research indicates that taking caffeine before a workout may: improve one’s physical performance. enhance their capacity for thought. may enhance their fat-burning rate.
Side effects of caffeine
As we are already aware of that, everything comes with pros and cons and it depends upon us how we take it:
- Caffeine overdose can cause caffeine intoxication, a condition in which the central nervous system is overstimulated. It is a transient, clinically relevant syndrome that appears after or right after caffeine consumption.
- Caffeine intake from energy drinks was found to have negative short-term cardiovascular consequences.
- Caffeine intake of more than 400 mg per day may result in symptoms such as insomnia, anxiety, restlessness, nausea, stomach pain, headaches, raised pulse, respiratory symptoms, agitation, hyperventilation, hallucinations, diuresis, and bleeding issues.
Does caffeine cause problems during menstruation?
- The short answer to the question “Does coffee relieve period cramps?” is no. Caffeine prevents a hormone from shrinking blood vessels, which can decrease the flow of blood and occur in the uterus. Coffee can aggravate stomach pain by causing inflammation and bloating. Therefore, consuming coffee may worsen cramps.
- Your periods may start earlier since caffeine in coffee is said to boost estrogen.
- Caffeine may cause more bleeding: The same Clinical Epidemiology study discovered that those who consumed more caffeine than those who consumed less of it bleed more heavily during their periods.
Myth about caffeine
- Caffeine causes dehydration.
- Caffeine is addictive.
- Caffeine causes insomnia.
- Caffeine has no health benefits.
Is it okay to drink coffee every day?
The FDA has stated that for healthy persons, 400 mg per day-roughly four or five cups of coffee-is a level that is not typically linked to harmful, adverse effects.
What are the sources of caffeine?
The sources of caffeine are
1. Tea
2. coffee
3. cocoa
4. espresso
5. chocolate
6. drinks
What is natural caffeine?
To add natural caffeine to various meals and beverages, the plant’s caffeine is extracted. Caffeine, which is present in more than 60 plant species worldwide, is found in the seeds of coffee, cacao, and kola nuts, in tea leaves and buds, in yerba mate leaves, and in the bark of yoco.
Do any fruits naturally contain caffeine?
More than 60 plant species around the world produce leaves, seeds, and fruits that naturally contain caffeine. Some foods and beverages have it added for flavor.
What does caffeine do to our bodies?
Because caffeine is a stimulant, it makes your brain and nervous system more active. Additionally, it promotes the body’s circulation of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Caffeine can help you feel alert and concentrated in modest quantities.