Table of Contents
TogglePulse polarography was developed to enhance the sensitivity of DC-polarography by reducing the background capacitive contribution to the current. This is achieved by eliminating the continuously varying potential ramp and replacing it with a series of potential steps of short duration applied at the end of the drop’s lifetime, thus, very little electrolysis and depletion occur.
What is pulse polarography?
A pulse is a very short lived signal. Pulse voltammetry or pulse polarography consists of the application of a series of potential pulses of increasing amplitudes for which the current response is measured near the end of each pulse on a fully grown Mercury drop.
Types of Pulse polarography
Pulse can be applied to the mercury drop in various fashions. On the basis of ways of applying the pulse, pulse polarography is of the following types.
- Normal pulse polarography(NPP)
- Differential pulse polarography(DPP)
- Square wave voltammetry(SWV)
- Reverse pulse voltammetry(RPV)
- Staircase voltammetry(SV)
Excitation signal in polarography
In polarography, an electrochemical cell’s working electrode is impressed with a changing potential excitation signal. Due to this applied excitation signal, a characteristic current response is produced, which is measured. In general, there are four types of commonly used excitation signals.
- Linear scan
- Differential pulse
- Square wave
- Triangular
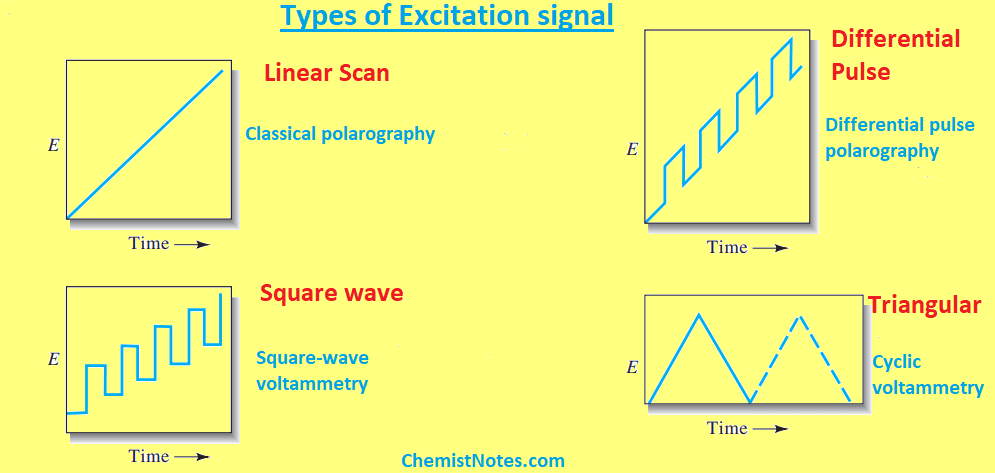
- The linear scan is a classical voltammetric excitation signal, in which the voltage applied to the electrochemical cell increases linearly as a function of time. The produced current can be measured either as a function of time or as a function of applied potential.
- In the case of differential pulse and square wave excitation signals, currents are recorded at various stages during the lifespan of the pulse.
- In the case of the triangular waveform, the potential oscillates between two values, first rising linearly to a peak and then falling linearly with the same slope to its starting value. Such signals are used in cyclic voltammetry.
Advantages of Pulse polarography
This technique is superior to traditional DC-polarography. It has the following advantages over DC-polarography.
- It has high detection limits
- The analysis time is very short
- There is very little contribution of the background current to the limiting current.
- This technique is very useful for the analysis of mixtures, as well as in multi-analysis.
- This provides a very improved signal with less or very little noise.
- This technique usually consumes fewer electroactive species.