Table of Contents
ToggleWittig rearrangement reaction, 1,2-Wittig rearrangement reaction, 2,3-Wittig rearrangement reaction, mechanism, and application have been discussed here.
wittig rearrangement reaction
Wittig rearrangement reaction has been classified into two types; 1,2-Wittig rearrangement and 2,3-Wittig rearrangement. Let’s discuss them with the mechanism.
1,2-Wittig rearrangement reaction:
When ether is treated with a strong base like alkyl lithium, ether is converted into a secondary alkoxide or alcohol via a 1,2- carbon shift. This reaction is known as 1,2-Wittig rearrangement. Let’s see some examples.
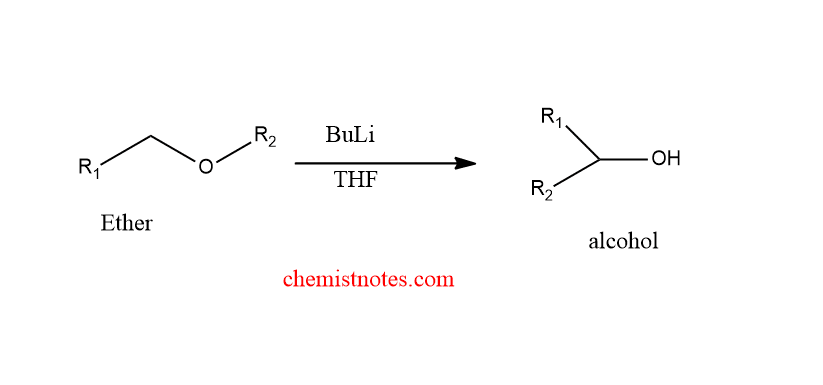
The migration tendency of groups depends on the group’s ability to stabilize a radical. Therefore, the migratory aptitude of groups is given below:
Methyl>Primary alkyl> Secondary alkyl> Tertiary alkyl
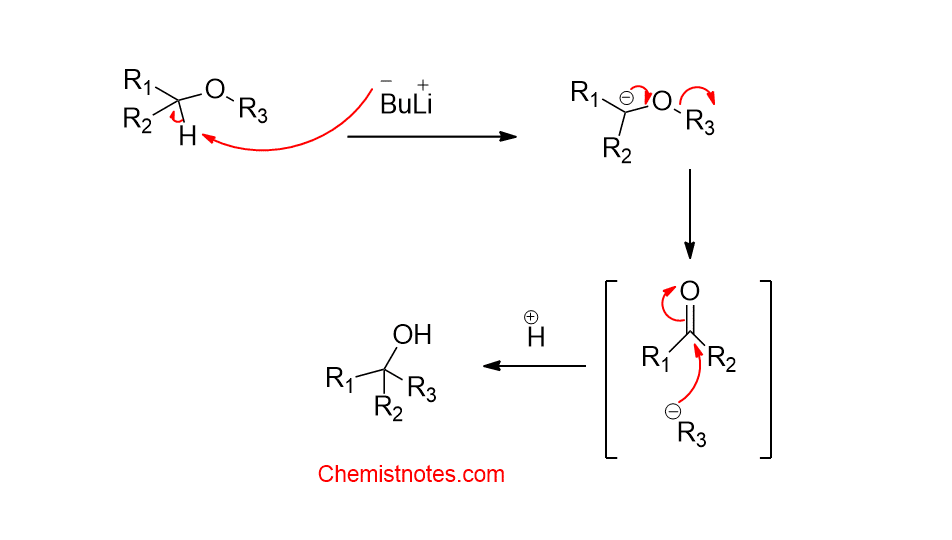
Mechanism of 1,2-Witting rearrangement:
1,2-Witting rearrangement is supposed to proceed via a radical mechanism and it is a stepwise reaction that consists of the following steps:
Step 1: Deprotonation of ether to form a carbanion
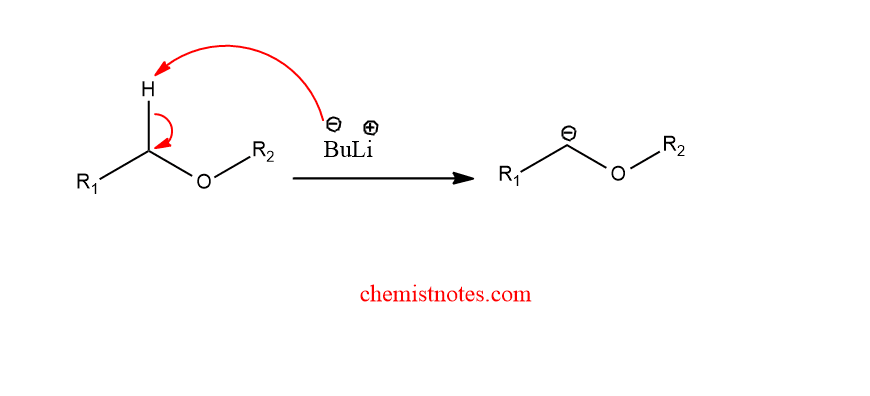
Step 2: Homolytic cleavage of an alkoxy carbanion to radical radical anion pair.
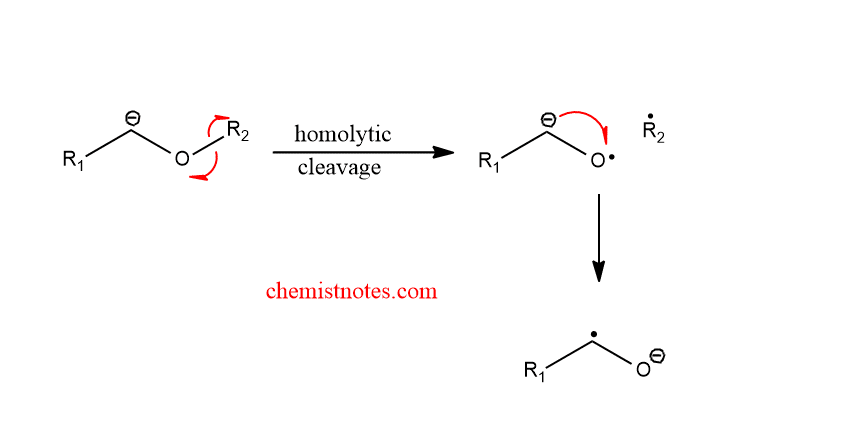
Step 3: Recombination of radical pairs
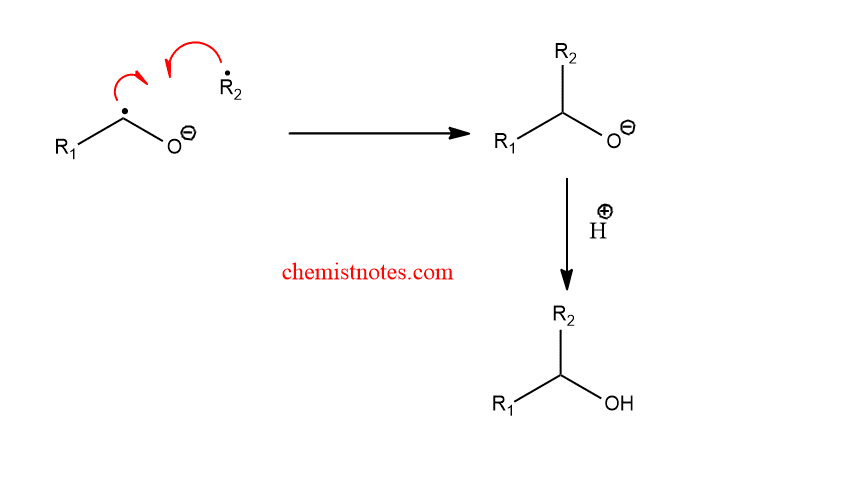
Alternatively, an ionic mechanism has been proposed in which the heterolytic cleavage of alpha-alkoxy carbanion takes place to form a ketone and anion. Then, the nucleophilic addition of anion to the carbonyl group takes place.
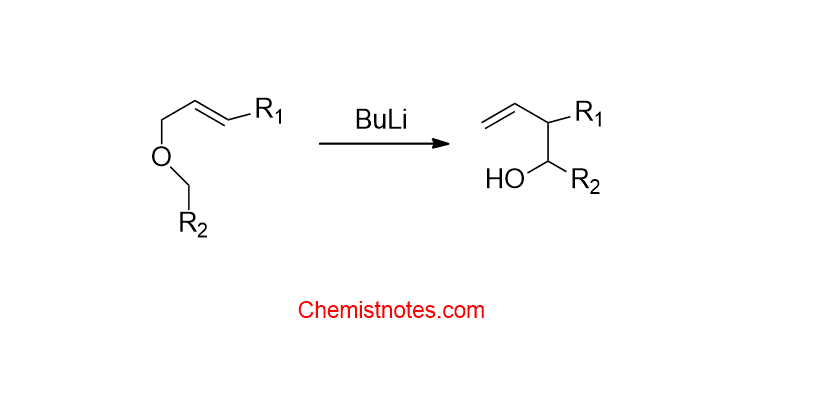
2,3- Wittig rearrangement reaction:
The conversion of allyl ethers or benzylic ethers into alcohol via the 2,3-sigmatropic rearrangement when allyl ether is treated with a base is called 2,3-Wittig rearrangement.’
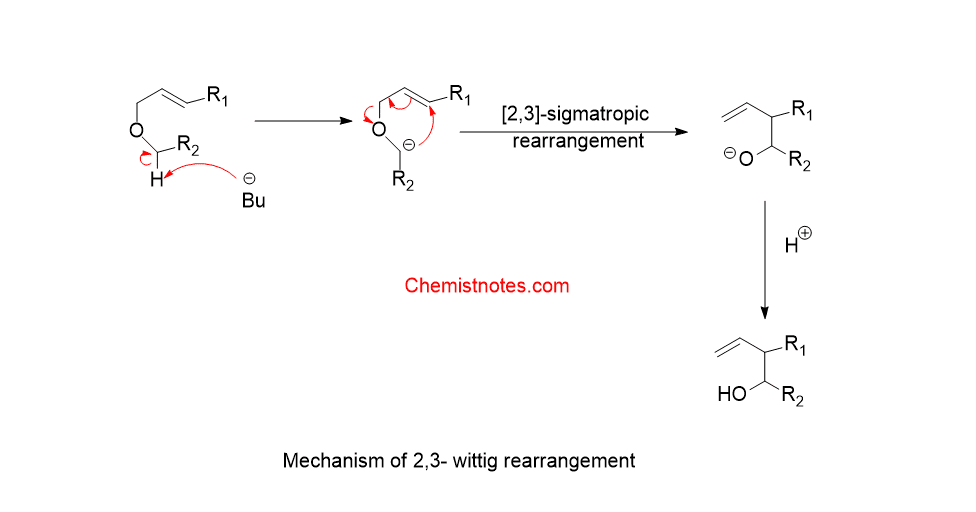
Mechanism of 2,3-wittig rearrangement:
The mechanism of this type of rearrangement is shown below:
application of wittig rearrangement
Wittig rearrangement is one of the important rearrangement reactions which is widely used in organic synthesis such as homoallylic alcohol derivatives.
References:
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010
- J.J. Li, Name Reactions, 4th ed.,© Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2009
- March, J., Advanced Organic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1986.
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987
Please comment if you have any problems related to this topic. Thank you.
Read also:
- Hofmann Rearrangement
- wagner meerwein rearrangement
- Pinacol pinacolone rearrangement
- Favorskii rearrangement
- Cope rearrangement
- Claisen Rearrangement
- Beckmann Rearrangement