Table of Contents
ToggleMeerwein Ponndorf Verley Reduction is popularly known as MPV reduction. This reaction was concurrently reported by Meerwein, Schmidt, and Verley in 1925, and by Ponndorf in 1926 respectively. Therefore, it is generally known as the Meeerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction or Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reaction.
MPV Reduction
The reduction of carbonyl compounds to corresponding alcohols by using an aluminum alkoxide as a catalyst and isopropanol as the reducing agent or hydride source is known as MPV reduction.
The catalyst generally includes Aluminum tri-isopropoxide{Al(O-i-Pr)3] and Aluminum tert-butoxide.
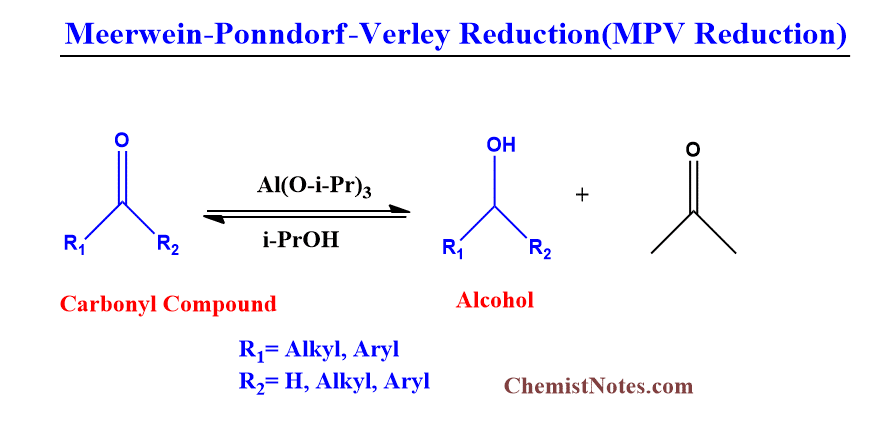
The MPV reaction has the following advantages:
- This reaction offers chemoselectivity.
- It takes place in mild reaction conditions
- It has operational simplicity and low cost.
- This reaction has no effect on other double bonds or triple bonds as well as other enolizable carbonyl compounds such as β-ketoester or β-diketones.
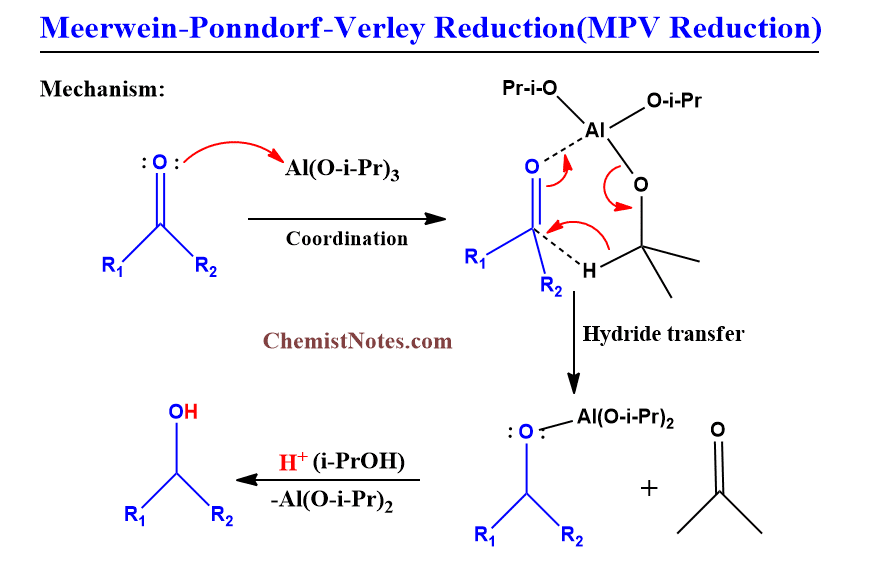
MPV Reduction mechanism
A six-membered cyclic transition state is produced when aldehyde or ketone is treated with aluminum tri isopropoxide in isopropanol solvents. The positive character of the carbonyl group is increased by the coordination of carbonyl compounds to the catalyst’s aluminum atom, which facilitates the transfer of hydrides from the isopropyl group to the carbonyl carbon center.
This reaction is supposed to take place in three steps:
- First of all, the coordination of carbonyl molecules to the aluminum metal of the alkoxide[Al(O-i-Pr)3] catalyst takes place which increases the positive character of the carbonyl group.
- Internal hydride transfer takes place from the alkoxide ligand to the carbon of the carbonyl group through a six-membered transition state forming a new alkoxide ligand and a new carbonyl compound.
- Alcoholysis of new alkoxide ligands forms alcohol and regenerates the catalyst.
Difference between Oppenauer oxidation and MPV reduction
The key difference between Oppenauer oxidation and MPV reduction is that the Oppenauer reaction is used to convert alcohols to aldehyde or ketone using aluminum alkoxide as a catalyst whereas MPV reduction is used to convert aldehyde or ketone back to alcohols using aluminum alkoxide as a catalyst.
Thus, the MPV reaction is regarded as the reverse reaction of Oppenaur oxidation in which ketone is used as a solvent but in the MPV reaction, alcohol is used as a solvent.
Application of MPV reduction
- This reaction can be used in the preparation of chiral alcohol which is very useful in Pharmaceutical and industrial chemistry.
- Since this reaction has no effect on double bonds or triple bonds, it can be used in the reduction of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
- This reaction can be used to create complex natural products and other biologically active molecules.
MPV reaction video
References:
- T. Okano, M. Matsuoka, H. Konishi, J. Kiji, Chem. Lett. 1987, 181–184
- Clay, J. M. Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction. In Name Reactions for Functional Group Transformations; Li, J. J., Corey, E. J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, 2007, pp 123−128. (Review).