Table of Contents
ToggleChugaev reaction mechanism is a concerted process, which has been discussed below along with its application and limitation. Chugaev reaction was first of all reported by Chugaev in 1899. It is a type of elimination reaction, also known as pyrolytic elimination.
Chugaev reaction
Alcohol reacts with carbon disulfide in presence of sodium hydroxide to give sodium xanthate, which on further alkylation with methyl iodide (generally) gives xanthate ester. This xanthate upon pyrolysis produces olefin or alkene. Thus, the conversion of alcohol into olefin by the corresponding xanthate esters is called Chugaev reaction. This reaction is also known as Chugaev elimination or Chugaev xanthate reaction.
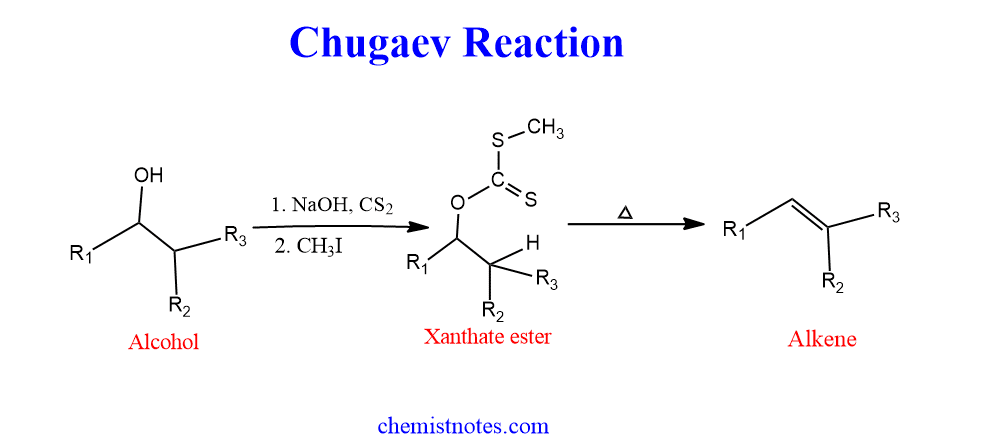
This reaction is very useful for the conversion of secondary and tertiary alcohol into an alkene. You may have questions on your head, why primary alcohol is not suitable for this purpose? right. Its because the xanthate ester of primary alcohol generally has high thermal stability therefore, it is difficult to decompose by heating.
- This pyrolysis takes place via an intramolecular cis-elimination without the rearrangement of carbon framework.
Chugaev reaction mechanism
The mechanism of Chugaev reaction is discussed below.
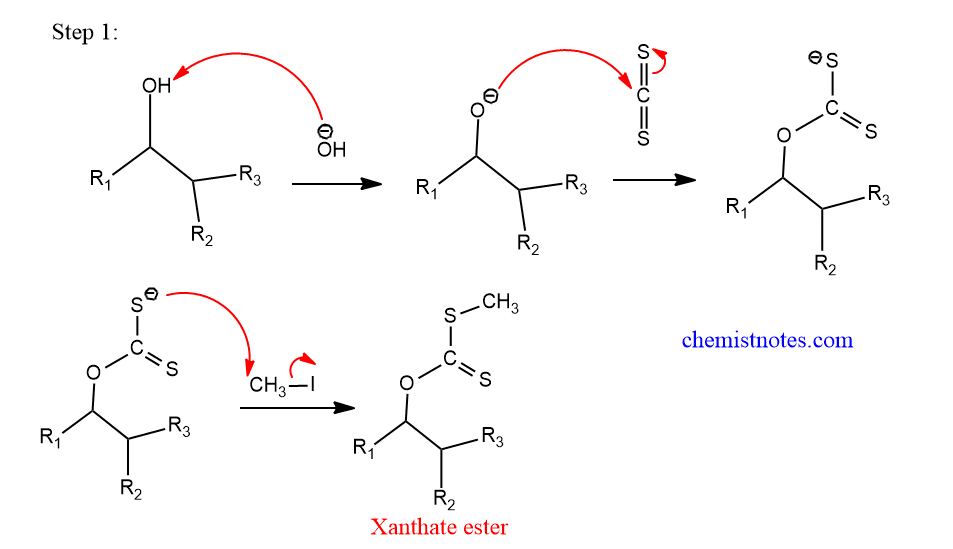
Step 1: Formation of xanthate ester
In this process, alcohol reacts with CS2 in presence of NaOH, followed by alkylation produces xanthate ester.
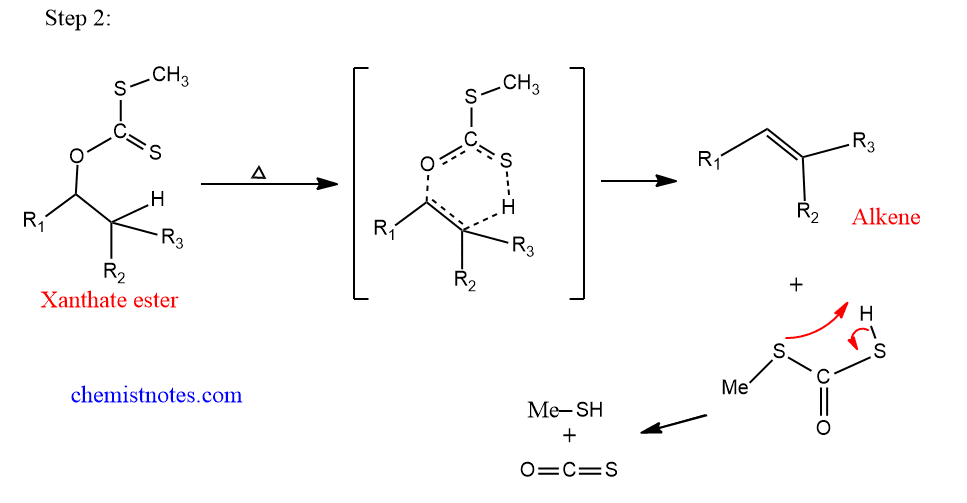
Step 2: Pyrolysis of xanthate ester.
This step is a concerted process, which takes place in presence of heat. Actually, this step is the Chagaev reaction in which the pyrolysis of xanthate ester takes place.
Some examples of Chugaev Reaction
Let’s see examples of this reaction.
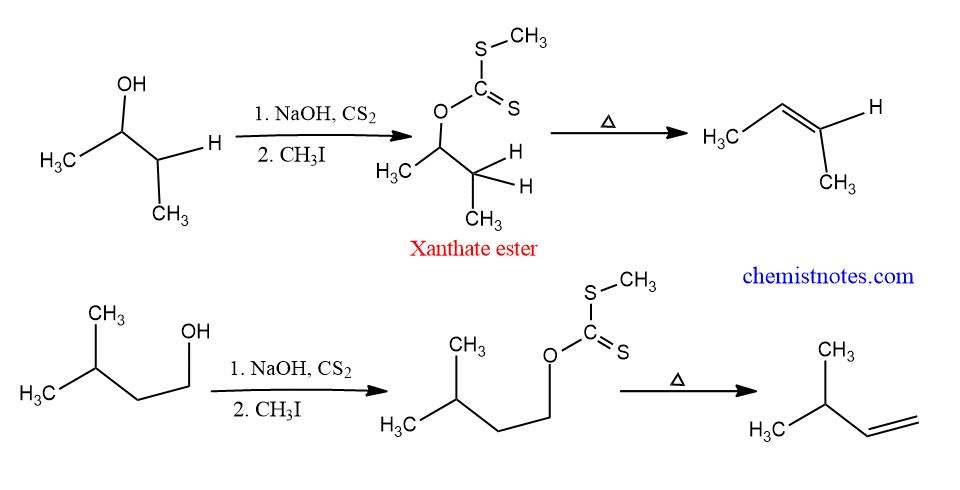
Application of Chugaev reaction
This reaction can be used for the preparation of different types of olefins including bornylene, menthene, etc.
Limitation
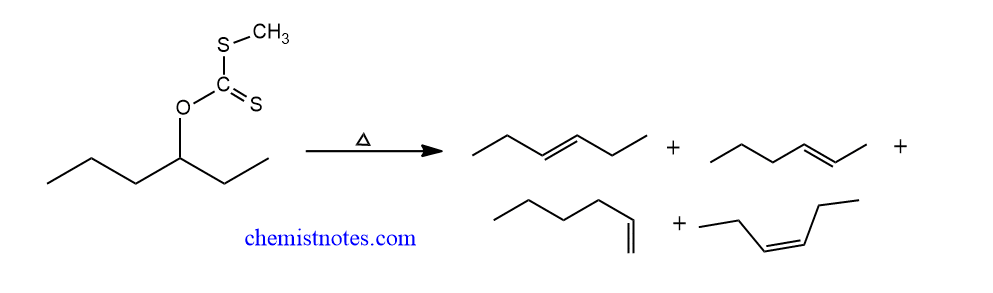
If the Beta-carbon contains more than one hydrogen or if the elimination is possible in more than one position, a mixture of isomeric olefins is produced. For example,
References
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010
- Laue T.,Plagens A.,Named Organic Reactions, Second edition, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005