Table of Contents
ToggleCarbylamine reaction mechanism, examples, and applications in organic chemistry are discussed here:
Carbylamine Reaction
Carbylamine reaction involves the reaction of a primary amine with chloroform in presence of alcoholic KOH that leads to the formation of isocyanide, and hence also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. In another word, carbylamine reaction is the synthesis reaction of isocyanide by the chemical reaction of primary amine, chloroform, and a base. This reaction is also known as used to detect the presence of primary (1o) amine.
Some of the examples of carbylamine reactions are:

Carbylamine Reaction Mechanism
The mechanism of carbylamine reaction can be carried into two following steps:
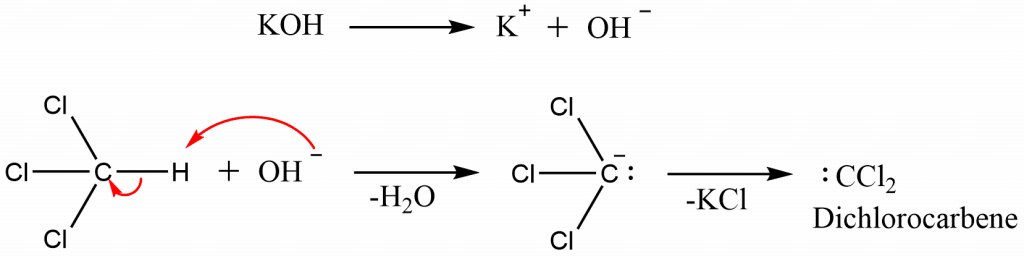
Step 1: Dehydrohalogenation of chloroform and the formation of reactive intermediate, dichlorocarbene
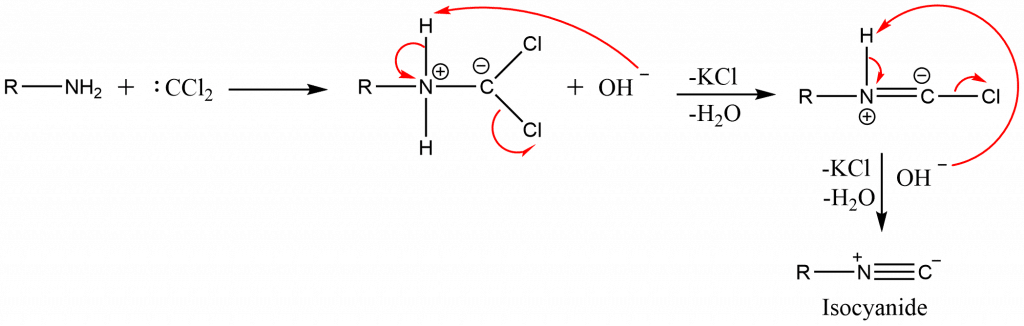
Step 2: Electrophilic addition of dichlorocarbene to amine followed by successive dehydrochlorination in presence of a base.
Application of Carbylamine reaction
- For the detection of primary amines.
- For the synthesis of an isocyanide
Carbylamine reaction Video
FAQs/MCQs
What is carbylamine reaction?
The reaction that involves the synthesis of isocyanide via the chemical reaction of primary amine, chloroform, and a base known as carbylamine reaction.
Hofmann Isocyanide test
When primary amine is heated with chloroform and alcoholic KOH, then it leads to the formation of isocyanide with an offensive smell. This test is known as the Hofmann isocyanide test and is used to detect primary amine.
References
- Ghosh, S.K., Advanced General Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, New Central Book Agency Pvt. Ltd., Kolkatta, 2007.
- Bahl, B.S., A., Advanced Organic Chemistry, S. Chand and company Ltd, New Delhi, 1992.
- Finar, I. L., Organic Chemistry, Vol. I and Vol. II, Prentice Hall, London, 1995.