Table of Contents
ToggleGeometric isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism that is also known as cis-trans isomerism or E-Z isomerism. Geometrical isomerism is not possible in 2-coordinated complexes, 3-coordinated complexes, or 4-coordinated tetrahedral complexes. This is because there are no cis positions in 2-coordinated complexes. But in 3-coordinated complexes and 4-coordinated tetrahedral complexes, all the coordinating positions are cis to each other, and there are no trans positions. However, cis-trans isomerism is very common in many 4-coordinated square planar complexes and 6-coordinated octahedral complexes.
In a cis isomer, two identical or similar groups are adjacent to each other whereas, in a trans isomer, they are opposite to each other.
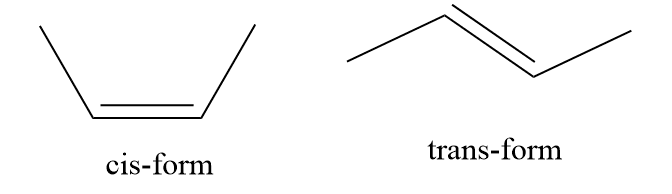
Geometrical isomerism in square planar complex
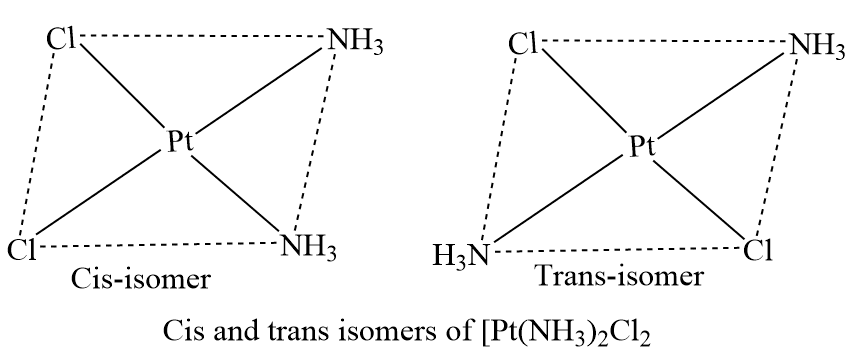
Type [Ma2b2]
There are cis and trans isomers of square planar complexes of the type [Ma2b2], where a and b are monodentate ligands. [Pt(NH3)2Cl2], [Pt(NH3)2(NO2)2], [Pt(Py)2Cl2], and other complexes of this type are examples. This cis-trans isomer of these compounds is represented below.
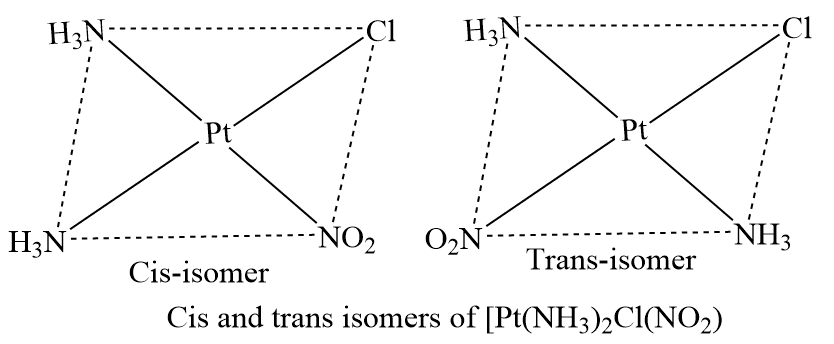
Type [Ma2bc]
Geometrical isomers of square planar complexes of the kind [Ma2bc], where a, b, and c are monodentate ligands.For example: [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] and [PdCl2Br]2–, have cis and trans isomers.
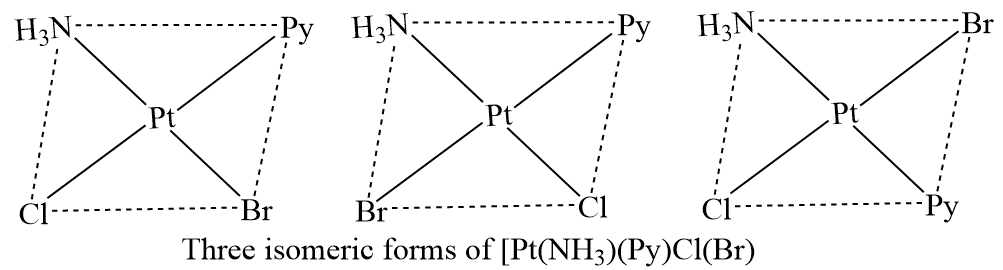
Type [Mabcd]
There are three isomeric forms of square planar complexes of the type [Mabcd]. [Pt(NH3)(Py)(Br)], for example, exists in three isomeric forms, as illustrated in the figure below. These isomeric forms can be made by selecting one ligand, such as NH3, and then transferring the remaining three ligands one at a time. Another example of square planar complexes with three isomeric forms is [Pt(NH3)(NH2OH)(Py)(NO2)]+.
Type, [M(AB)2]
Square planar complex of the type, [M(ab)2], where AB is an unsymmetrical, bidentate ligand, such as glycinato ligand, exist as cis and trans isomers. For example, [Pt(gly)2] exist as cis and trans isomers.
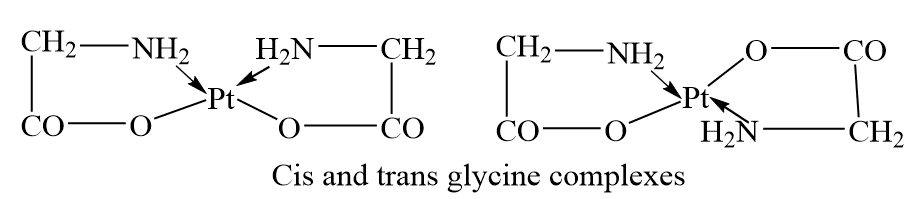
Types, [Ma4] and [Ma3b]
Square planar complexes of the types, [Ma4] and [Ma3b], donot show geometrical isomerism, since all the possible spatial arrangement of four ligands round the central metal atom is the same.